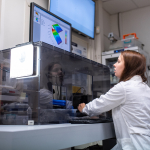
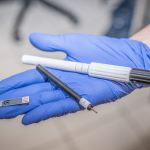
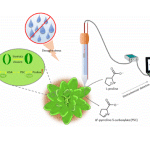
Naše výzkumná skupina se specializuje na dva hlavní výzkumné směry, a to syntézu nanomateriálů a jejich následnou charakterizaci. Druhým významným směrem našeho výzkumu je elektrochemická analýza.V oblasti syntézy nanomateriálů se zaměřujeme na přípravu široké škály materiálů, začínající od uhlíkatých, jako je grafen oxid, a konče nanokompozity. Naše výzkumné úsilí směřuje nejen k vytváření těchto materiálů, ale také k jejich důkladné charakterizaci. Tyto nanomateriály pak zkoumáme v kontextu jejich aplikací, a to zejména v oblasti zemědělství a vývoje biosensorů. Naše laboratoř elektrochemie je zase zaměřena na vývoj biosensorů, přípravu elektrod a využití skenovací elektrochemické mikroskopie v širokém spektru analýz, sahajících od pečlivého zkoumání materiálů až po živé buňky. Naše hlavní oblasti zájmu zahrnují detekci hormonů, sacharidů, organických kyselin a aminokyselin.
Další část výzkumu je zaměřena na studium produkce a imobilizace biotechnologicky významných enzymů, jejichž aplikační potenciál je testován v bioreaktoru na reálných vzorcích například vod kontaminovanými rezidui léčiv či syntetickými barvivy apod.
Pro detekci elektrochemicky neaktivních látek nebo pro výrazné zvýšení odezvy analytu lze využít konjugaci s elektroaktivními značkami (např. na bázi kvantových teček).
K dalším oblastem našeho zájmu patří vývoj senzorů a biosenzorů (detekce platinových cytostatik, studium metylace DNA ve spojení se vznikem nádorových onemocnění, zjišťování kontaminace životního prostředí těžkými kovy apod.). A nedílnou součastí našeho aplikovaného výzkumu jsou moderní apikace v zemědělství.
Doc. RNDr. Lukáš Richtera, Ph.D.
Vedoucí výzkumné skupiny syntézy a chemické analýzy
Akademický pracovník – docent
Kontakt
E-mail: oliver@centrum.cz
Researcher ID: N-9991-2014
ORCID: 0000-0002-8288-3999
Scopus ID: 12040049600
Laboratoře a jejich vedoucí
- Laboratoř elektrochemie – Ing. Eliška Birgusová
- Laboratoř syntézy a charakterizace nanomateriálů – Ing. Jana Pekárková, Ph.D.
- Laboratoř environmentální chemie a enzymologie – Ing. Martina Vršanská, Ph.D.
- CHNS/O analýza – RNDr. Lenka Vaňková, Ph.D.
Členové týmu
- Ing. Zuzana Bytešníková, Ph.D. (mateřská dovolená)
- Ing. Jana Pekárková, Ph.D.
- Ing. Eliška Birgusová
- Mgr. Stanislava Voběrková, Ph.D.
- Ing. Martina Vršanská, Ph.D.
- RNDr. Lenka Vaňková, Ph.D.
- Sanam Garehbaghi, MSc.
- MSc. Arezoo Saadati
- MSc. Hoang-Anh Cao
- MSc. Nghiem Xuan Duc
- Ing. Ester Kovaříková
- Mgr. Eva Jansová, Ph.D.
Ocenění
- Ing. Eliška Birgusová získala za práci s název ,,Elektrochemický biosenzor pro detekci metylace DNA“ zvláštní cenu poroty. Ocenění získala v celostátní soutěži o nejlepší studentskou vědeckou práci v oboru analytická chemie „O cenu Karla Štulíka 2021“
- Ing. Eliška Birgusová získala za práci s názvem ,,Elektrochemická detekce jablečno-mléčné fermentace’’ zvláštní cena poroty, celostátní soutěži o nejlepší studentskou vědeckou práci v oboru analytická chemie „O cenu Karla Štulíka 2022“
- Ing. Eliška Birgusová obdržela v roce 2023 talentové stipendium v rámci soutěže Mendelu P.hD. talent za projekt s názvem ,,Electrochemical detection and removal of estrogen from the water environment “
- Ing. Eliška Birgusová, první místo konference MendelNet 2024 Molecular imprinting particles as a solution for estradiol water contamination
- Ing. Zuzana Bytešníková, Ph.D, Cena rektora 2023 cena za mimořádné výsledky tvůrčí činnosti mladých do 35 let
Projekty
- TAČR Gama: Technologie přípravy antimikrobiálních grafenových nanoformulací pro polymerní kompozitní filamenty pro 3D tisk (2021, Bytešníková)
- IGA projekt: Elektrochemický biosensor pro monitorování estrogenů ve vodních systémech (2023, Birgusová)
- IGA projekt:Molekulárně imprintované částice pro analýzu estrogenních polutantů (2024, Birgusová)
- TAČR TREND (FW01010202): Výzkum a vývoj inovativních řešení v laboratorní diagnostice (2020-2022, Richtera)
Publikace
- Kudr, Jiří; Haddad, Yazan; Richtera, Lukáš; Heger, Zbyněk; Černák, Mirko; Adam, Vojtěch; Zítka, Ondřej. Magnetic Nanoparticles: From Design and Synthesis to Real World Applications. Nanomaterials (Basel), 2017, Vol. 7, Issue 9, pp 243. DOI: 10.3390/nano7090243.
- Skaličková, Sylvie; Milosavljević, Vedran; Číhalová, Kristýna; Horký, Pavel; Richtera, Lukáš; Adam, Vojtěch. Perspective of selenium nanoparticles as a nutrition supplement. Nutrition, 2017, Vol. 33, pp 83–90. DOI: 10.1016/j.nut.2016.05.001.
- Kudr, Jiří; Richtera, Lukáš; Xhaxhiu, Kledi; Hynek, David; Heger, Zbyněk; Zítka, Ondřej; Adam, Vojtěch. Carbon dots based FRET for the detection of DNA damage. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2017, Vol. 92, pp 133–139. DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.01.067.
- Ashrafi, Amir M.; Bytešníková, Zuzana; Barek, Jiří; Richtera, Lukáš; Adam, Vojtěch. A critical comparison of natural enzymes and nanozymes in biosensing and bioassays. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2021, Vol. 192, 113494. DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113494.
- Vaňová, Veronika; Mitrevska, Katerina; Milosavljević, Vedran; Hynek, David; Richtera, Lukáš; Adam, Vojtěch. Peptide-based electrochemical biosensors utilized for protein detection. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2021, Vol. 180, 113087. DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113087.
- Durovic, A.; Stojanovic, Z.; Kravic, S.; Kos, J.; Richtera, L.; Electrochemical Determination of Vitamin D3 in Pharmaceutical Products by Using Boron Doped Diamond Electrode . Electroanalysis 2019, in press, . DOI: 10.1002/elan.201900532 .
- Bytesnikova, Z.; Richtera, L.; Smerkova, K.; Adam, V.; The graphene oxide as a tool for antibiotic resistance genes removal: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 20148-20163. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-019-05283-y.